A parenting plan is meant to provide structure and consistency for both parents and children. When one parent refuses to follow it, things can quickly become stressful. Missed visitations, unapproved schedule changes, or ongoing conflicts can disrupt routines and put unnecessary strain on everyone involved.
According to Washington State Courts, the majority of child custody cases are resolved outside litigation, meaning most parents in Washington likely settle parenting plans through mediation or agreement rather than court battles. However, understanding the legalities around parenting plans can better prepare you for any future disputes.
At Northwest Family Law, we understand that these situations are about stability for your child and peace of mind for you. That’s why we take a holistic approach, offering not only legal guidance but also connections to financial planners, child therapists, and other professionals who can help you move forward.
Key Takeaways
- Parenting plan violations can include missed visits or refusing to follow the agreement.
- Courts may issue warnings, fines, custody changes, or jail time.
- Document violations, try mediation, and take legal action if needed.
- Clear communication and consistency help prevent future issues.
What is a Parenting Plan and Why is It Important?
A parenting plan is a written agreement between separated or divorced parents that outlines how they will raise their children.
It covers aspects like living arrangements, visitation schedules, decision-making responsibilities, and how to handle disputes. The goal is the betterment of the child’s well-being by providing a clear and consistent framework for co-parenting.
Understanding the Legal Binding Nature of Parenting Plans
In many jurisdictions, parenting plans become legally binding once approved by a court. This means both parents are obligated to follow the terms set out in the plan. If one parent fails to comply, they may face legal consequences, such as contempt of court charges or modifications to custody arrangements.
Having a legally binding plan helps prevent misunderstandings and provides a clear path for enforcement if disputes arise.
Key Components of a Parenting Plan
A comprehensive parenting plan typically includes:
- Physical Custody Arrangements: Details about where the child will live and the schedule for time spent with each parent.
- Legal Custody Provisions: Information on which parent has the authority to make important decisions regarding the child’s education, health care, and religious upbringing.
- Visitation Schedules: Specific times and dates for visitations, including holidays, vacations, and special occasions.
- Communication Guidelines: Protocols for how parents will communicate with each other and with the child, including frequency and preferred methods.
- Dispute Resolution: Steps to resolve disagreements, such as mediation or counseling, before seeking court intervention.
5 Types of Parenting Plan Violations
A parenting plan violation happens when one parent doesn’t follow the custody agreement or visitation schedule outlined in the plan. Some violations are minor misunderstandings, while others can have serious legal consequences. Common violations include:
- Missing scheduled visitation: Failing to show up for pick-ups or repeatedly arriving late disrupts the child’s routine.
- Denying the other parent’s visitation: One parent refuses to allow court-ordered visits, sometimes as an emotional response or act of retaliation.
- Changing the child’s residence without approval: Relocating a child without informing the other parent can lead to legal action.
- Blocking communication with the child: Ignoring calls, texts, or messages when the other parent tries to reach their child.
- Ignoring decision-making agreements: Making major choices about the child’s education, healthcare, or religion without consulting the other parent.
Accidental vs. Intentional Violations
Some violations happen due to emergencies, scheduling conflicts, or simple miscommunication. Others are deliberate attempts to interfere with the co-parent’s rights. Courts often distinguish between the two by labeling them as accidental violations or repeated/intentional violations. The latter of which can lead to charges.
How Parenting Plan Violations Affect the Child
Here are some examples of how parenting plan violations can affect a child:
- Emotional distress: Children thrive on routine. Disrupting their schedule can create anxiety and instability.
- Strained parent-child relationships: When one parent denies access to the other, the child may develop resentment or confusion about their role in the family.
- Legal battles and stress: Ongoing custody disputes add unnecessary tension and can force children into difficult legal situations, such as court interviews or therapy assessments.
What Are the Legal Consequences of Violating a Parenting Plan in Washington?
Failing to adhere to a court-ordered parenting plan can lead to serious legal repercussions. According to Washington law, a parent found in contempt for violating the plan may face penalties such as fines, modifications to the parenting plan, or even jail time.
Can a Parent Get a Warning for Violating a Parenting Plan?
Not every violation leads to immediate legal action. If a parent makes an honest mistake or has a valid excuse, the court may issue a warning or recommend mediation. Judges often encourage parents to resolve minor issues outside of court before taking legal steps.
However, if a pattern of violations emerges, the court is more likely to intervene. Ignoring a parenting plan repeatedly signals an unwillingness to cooperate, which can have serious consequences.
What Happens If a Parent Repeatedly Ignores a Custody Agreement?
When a parent consistently violates the parenting plan, legal enforcement becomes necessary. Common consequences include:
- Contempt of court: The violating parent may be held in contempt, which can result in fines, community service, or, in extreme cases, jail time.
- Modification of custody or visitation rights: Courts may limit parenting time or even change custody arrangements if one parent continues to break the agreement.
- Make-up parenting time: Judges may order the violating parent to provide additional time to the other parent to compensate for missed visits.
- Financial penalties: The violating parent may be required to cover court costs, attorney fees, or other expenses caused by their non-compliance.
Can a Parent Go to Jail for Violating a Parenting Plan?
In extreme cases, yes. While jail time is rare, it can happen if a parent repeatedly disobeys court orders, especially in cases of:
- Parental kidnapping: Taking a child across state lines or out of the country without permission.
- Repeated, willful violations: Ignoring multiple court orders despite previous warnings and penalties.
- Interfering with custody: Preventing the other parent from seeing the child, even after legal intervention.
4 Steps You Can Take If the Other Parent Violates the Parenting Plan
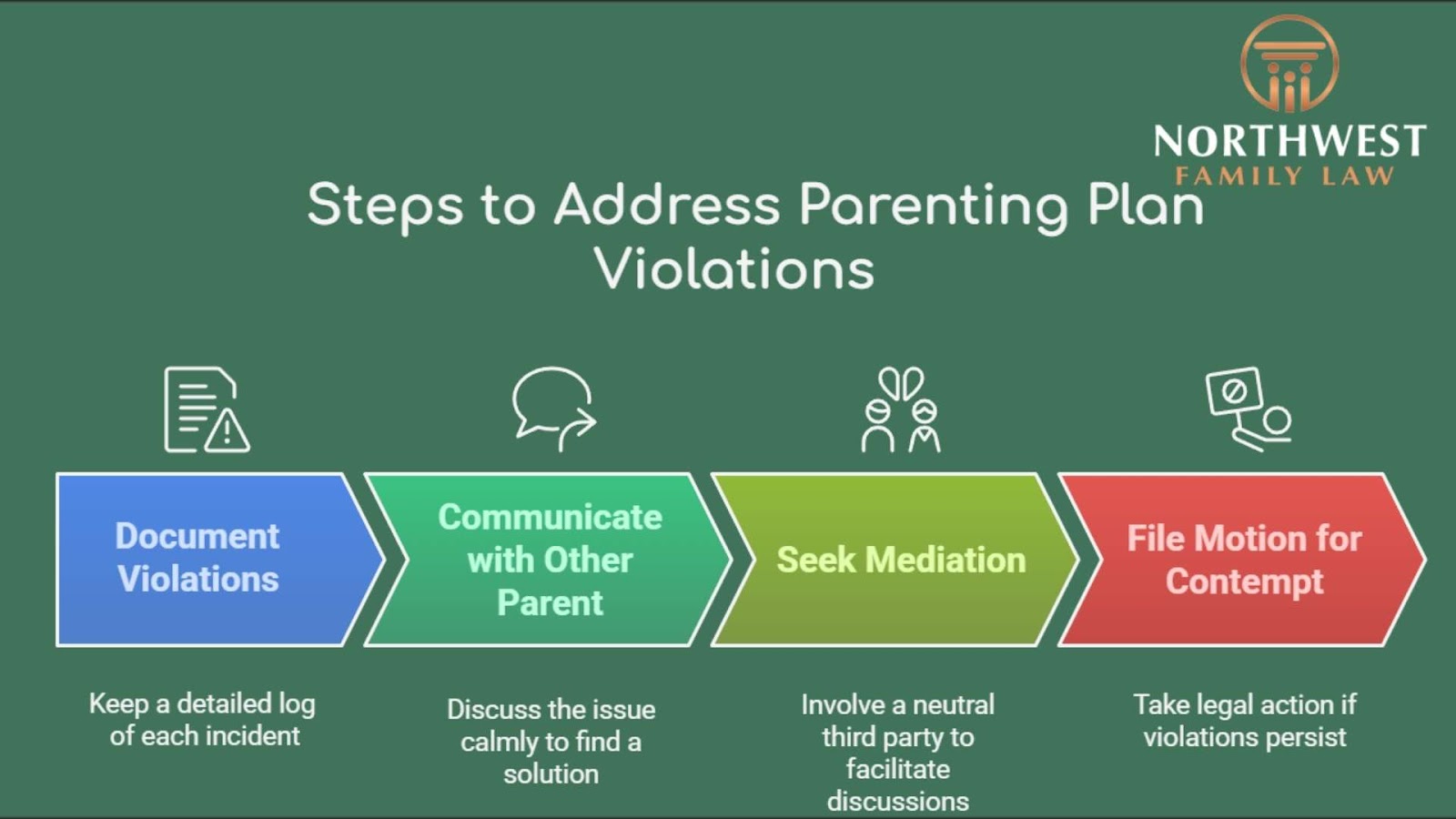
When a parent violates a parenting plan, it can be frustrating and disruptive. Addressing the issue promptly and effectively is vital to maintain stability for your child.
1. Documenting Violations
Accurate records are important when addressing violations. Keep a detailed log of each incident, noting dates, times, and descriptions. Save any related communications, such as texts or emails, as evidence. This documentation will be helpful if legal action becomes necessary.
2. Communicating with the Other Parent
Open dialogue can often resolve issues without escalation. Approach the other parent calmly to discuss the violation, aiming to understand their perspective and find a mutually agreeable solution. This step can prevent misunderstandings and foster cooperation.
3. Seeking Mediation
If direct communication doesn’t resolve the issue, consider mediation. A neutral third party can facilitate discussions and help both parents reach an agreement, keeping the child’s best interests at the forefront.
4. Filing a Motion for Contempt
If violations persist, you can file a motion for contempt in court. The court will assess the situation and may impose penalties.
How Can You Prevent Future Parenting Plan Violations?
Avoiding parenting plan conflicts starts with clear communication, realistic agreements, and proactive planning. Taking steps to prevent violations helps reduce stress and keeps the focus on the child’s well-being.
Establishing Clear Communication
Miscommunication is one of the biggest reasons parenting plans break down. Setting up consistent and respectful ways to communicate can prevent misunderstandings.
- Use a co-parenting app: Platforms like OurFamilyWizard or TalkingParents create a written record of conversations, reducing misinterpretations.
- Keep messages brief and to the point: Stick to facts and avoid emotional language that could escalate tensions.
- Agree on preferred methods of contact: Some parents communicate better through email, while others prefer texts or scheduled phone calls. Finding what works for both parties keeps communication smooth.
Reviewing and Updating the Parenting Plan
Life changes may necessitate adjustments to the plan. Washington State law allows for modifications when a substantial change in circumstances occurs, which makes sure the plan remains in the child’s best interest.
- Schedule regular check-ins: Discuss any necessary adjustments as your child grows.
- Consider life changes: Relocation, new jobs, or shifting school schedules might require modifications.
- Work through mediation if needed: If disagreements arise, a mediator can help parents reach fair solutions without going to court.
Following a Consistent Routine
Children thrive on stability. Sticking to the agreed-upon schedule helps them feel secure and reduces conflict between parents.
- Prioritize punctuality: Being on time for pick-ups and drop-offs shows respect for the agreement and the child’s routine.
- Honor the visitation schedule: Skipping or rescheduling visits too often can cause frustration and lead to disputes.
- Encourage flexibility when necessary: Unexpected events happen, but parents should make an effort to be accommodating while still respecting the agreement.
Seeking Professional Support When Necessary
Sometimes, outside help is needed to maintain a healthy co-parenting dynamic.
- Co-parenting counseling: A therapist or counselor can help go through challenges and improve cooperation.
- Legal guidance: If disputes continue, consulting a family law attorney makes sure parents understand their rights and obligations.
- Support groups: Connecting with other co-parents can provide valuable insight and emotional support.
When Should You Seek Legal Help for Parenting Plan Violations?

Some parenting plan disputes can be worked out between co-parents, but ongoing violations may require legal intervention. Understanding when to involve a lawyer or the court can help protect your parental rights and secure the best outcome for your child.
Repeated or Severe Violations
When violations become a pattern, legal action may be necessary. Courts take persistent non-compliance seriously. Judges may impose penalties, adjust custody arrangements, or enforce compliance through court orders.
Unsuccessful Mediation Attempts
Mediation can help resolve parenting disputes without a courtroom battle. However, it only works if both parents are willing to cooperate. If one parent refuses to negotiate or ignores agreements reached in mediation, legal enforcement may be the only option.
Endangerment or Parental Neglect
If a parent’s actions put the child at risk, immediate legal intervention is necessary. Signs that a violation has escalated to a serious legal issue include:
- Substance abuse or reckless behavior around the child.
- Verbal, emotional, or physical abuse.
- Exposing the child to unsafe living conditions.
- Neglecting the child’s basic needs, such as medical care or education.
Protect Your Parenting Rights
When a parenting plan is ignored, your child’s stability is at stake. At Northwest Family Law, we provide more than legal solutions, we offer personalized support to help you move forward with confidence.
If your co-parent isn’t following the agreement, take action today. Schedule a consultation to protect your rights and your child’s future.

